QR Code
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/QR_code
QR Code: Quick Response code
The processor locates the three distinctive squares at the corners of the QR code image, using a smaller square (or multiple squares) near the fourth corner to normalize the image for size, orientation, and angle of viewing.
The small dots throughout the QR code are then converted to binary numbers and validated with an error-correcting algorithm.
Storage
The amount of data that can be stored in the QR code symbol depends on the datatype (mode, or input character set), version (1, …, 40, indicating the overall dimensions of the symbol, i.e. 4 × version number + 17 dots on each side), and error correction level.
The maximum storage capacities occur for version 40 and error correction level L (low), denoted by 40-L
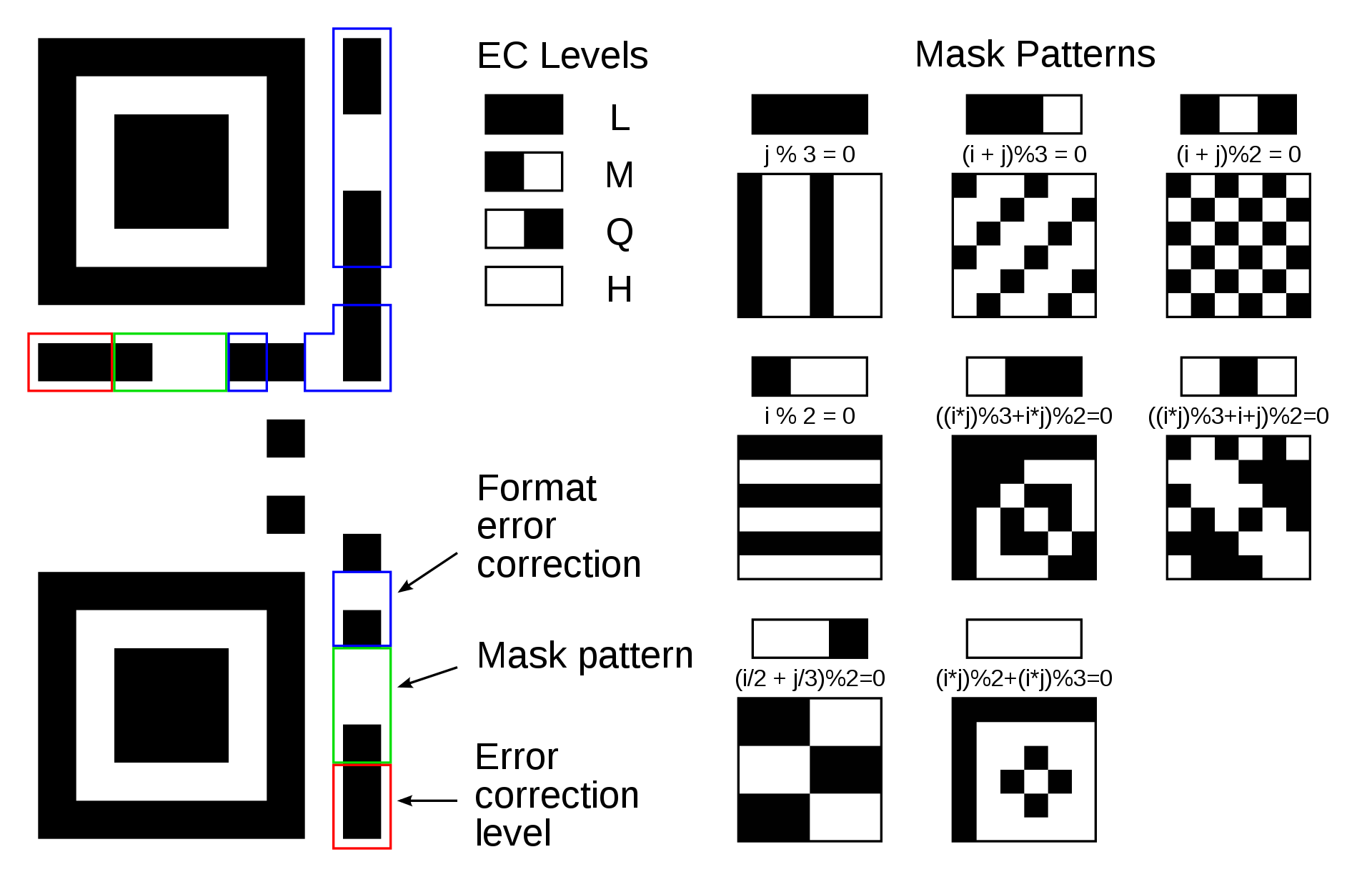
Error Correction
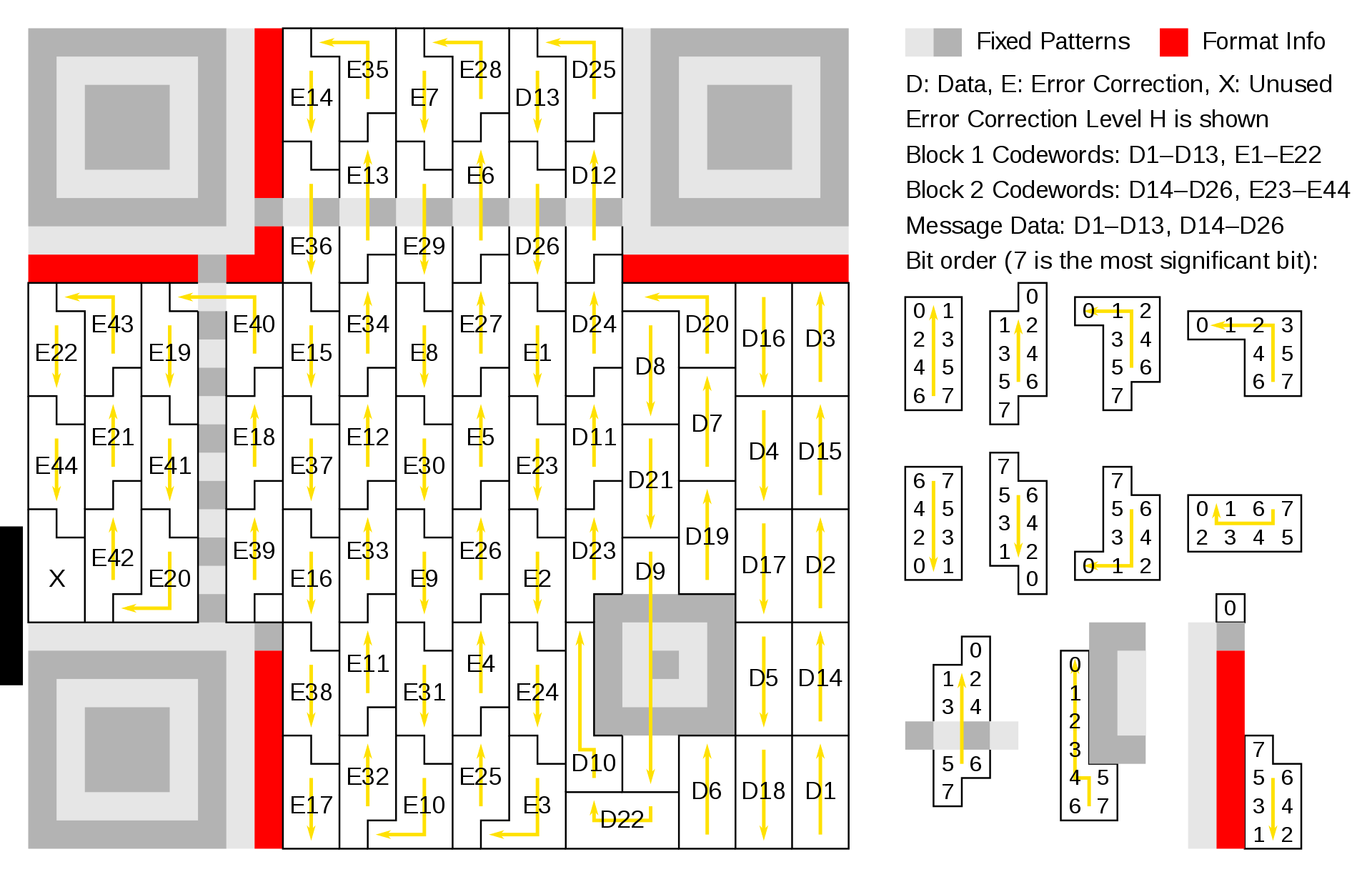
QR codes use Reed–Solomon error correction over the finite field $\displaystyle \mathbb {F} _{256}$, the elements of which are encoded as bytes of 8 bits.
| Level L (Low) | 7% of data bytes can be restored. |
| Level M (Medium) | 15% of data bytes can be restored. |
| Level Q (Quartile) | 25% of data bytes can be restored. |
| Level H (High) | 30% of data bytes can be restored. |
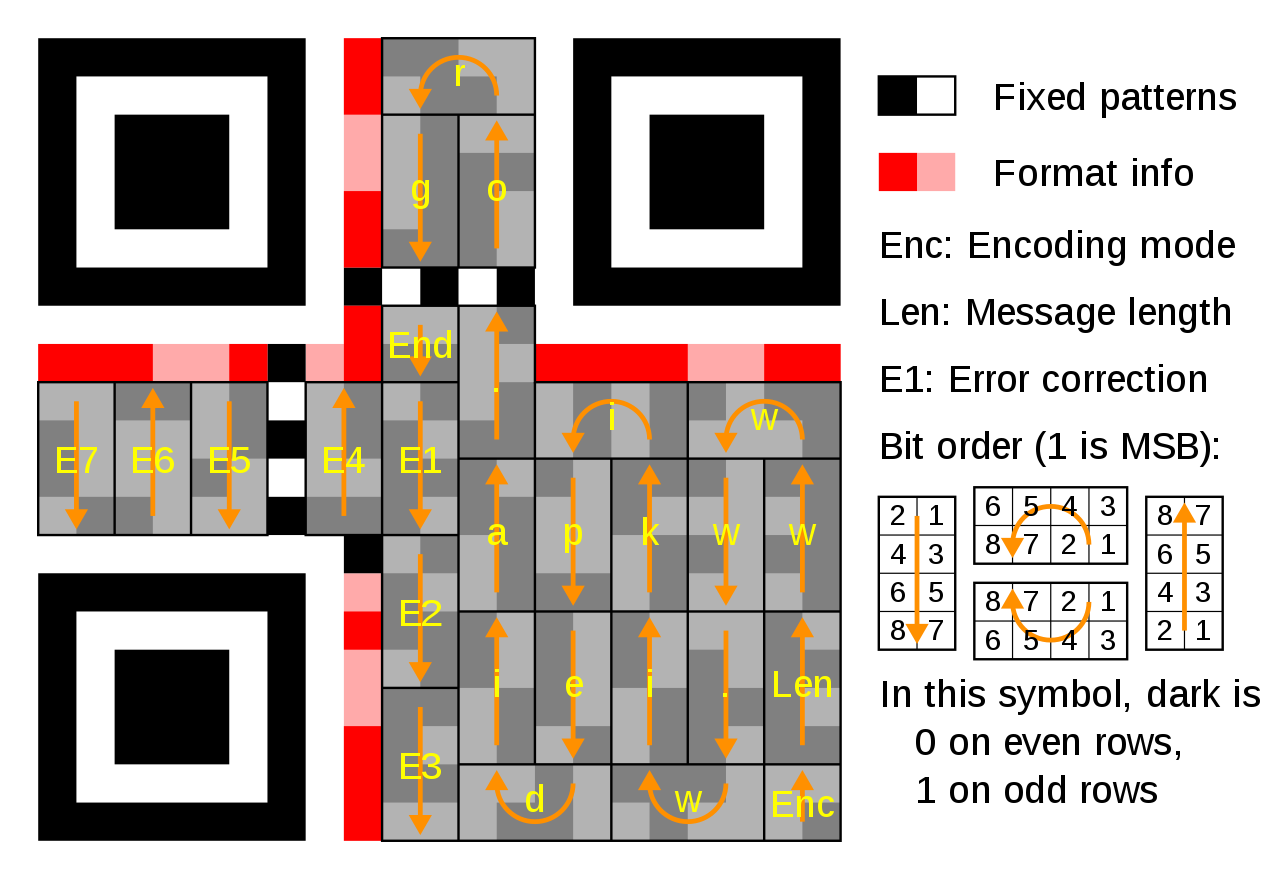
Encoding